Varicose veins are a common vascular condition that typically appear as bulging, twisted veins just beneath the skin’s surface. These veins are most often found in the legs, ankles, and feet, and can cause discomfort or pain for the affected individuals. The development of varicose veins is linked to various factors, and this article will explain how to identify, prevent, and treat the condition.
What Are Varicose Veins?
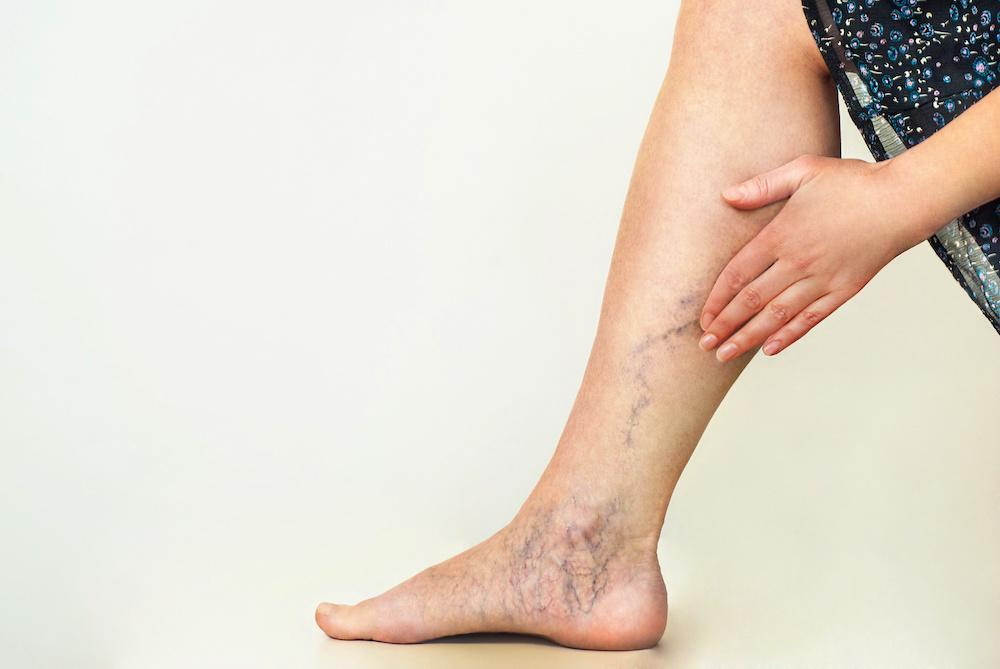
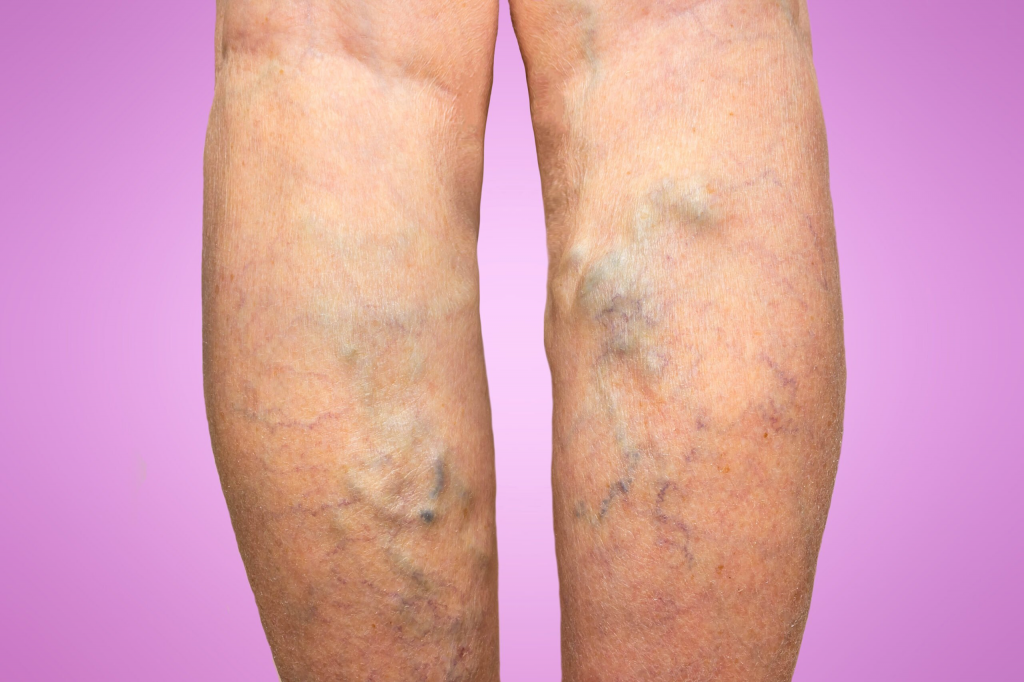
Varicose veins refer to veins that are enlarged and twisted, often appearing blue or purple, like cords running just beneath the skin’s surface. They usually affect the legs, ankles, and feet. When these veins become severely swollen and are surrounded by small blood vessels (called spider veins), they are considered superficial varicose veins. These veins can cause symptoms such as swollen ankles, itchy skin, and localized aching, but in most cases, they are harmless.
Unlike superficial veins, deep veins are harder to observe and are typically associated with more severe conditions, such as swelling or aching in the entire leg, and may serve as sites for blood clot formation. Though deep varicose veins are not easily visible, they require attention and treatment.
Spider Veins vs. Varicose Veins
Spider veins are smaller than varicose veins and do not bulge out. They resemble spider webs or tree branches and are typically red, blue, or purple in color. Unlike varicose veins, spider veins are not technically veins, but rather capillaries, venules, or arterioles. Spider veins rarely cause pain or other symptoms, unless the appearance is bothersome.
Causes of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are typically caused by several factors, with the most common being pregnancy, obesity, and prolonged standing. During pregnancy, the increased blood volume and the pressure exerted by the uterus on the veins of the legs can contribute to the development of varicose veins. Additionally, prolonged sitting or standing, lack of exercise, and constipation can all worsen varicose vein formation. As people age, their veins lose elasticity, which increases the risk of varicose veins. Family history also plays a significant role—if other family members have varicose veins, you may be more likely to develop them as well.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Early symptoms of varicose veins may include only cosmetic changes, but as the condition progresses, it may lead to various discomforts. Common symptoms include:
- Leg swelling
- Bulging veins that appear blue or purple
- Pain, heaviness, or burning sensation in the legs
- Increased pain after standing for long periods
- Nighttime leg cramps
In more severe cases, varicose veins can cause skin discoloration, ulcers, and bleeding.
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
The treatment for varicose veins ranges from simple home remedies to more invasive surgeries. Common treatment methods include:
- Compression Stockings: Compression stockings help by compressing the legs, which prevents blood from pooling and reduces symptoms.
- Elevating Legs: Elevating your legs several times a day can help reduce swelling.
- Medications: While some creams and lotions claim to alleviate symptoms of varicose veins, their effectiveness is not proven.
- Surgical Treatment: For more severe varicose veins, surgery to remove the veins or laser treatment may be necessary.
Prevention of Varicose Veins
Although genetic factors cannot be avoided, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can prevent or mitigate many issues related to varicose veins. Here are some effective preventive measures:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise helps maintain healthy leg muscles and improves blood circulation.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Keeping your weight in check reduces pressure on the veins.
- Avoid Tight Clothing and High Heels: These types of clothing and shoes can restrict blood flow, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
- Avoid Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Try to avoid holding the same position for extended periods, and remember to move around or elevate your legs regularly.
When to See a Doctor?
If your varicose veins are mild, simple treatments like compression stockings may suffice. However, if the symptoms become severe or the appearance of your veins is troubling, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider. Immediate medical attention should be sought if symptoms such as skin ulcers, redness, warmth, or pain occur.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are common, but they don’t always lead to serious health problems. By recognizing and managing the symptoms, and adopting appropriate treatment and preventive measures, individuals can greatly improve their quality of life. If the condition worsens or complications arise, professional medical treatment should be sought promptly.