What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury, infection, or disease. Your immune system triggers inflammation as a defense mechanism to help protect your body. This process can be beneficial in healing, but when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to long-term health issues.
Inflammation can be divided into three main categories:
- Acute Inflammation: This type appears suddenly and usually resolves within a few days or weeks once the cause (such as infection or injury) is removed.
- Chronic Inflammation: This type lasts for more than six weeks and is often associated with conditions such as autoimmune diseases, prolonged stress, and obesity. Chronic inflammation can lead to more serious health issues.
- Subacute Inflammation: Occurs between acute and chronic inflammation and usually lasts from two to six weeks.
Symptoms of Inflammation
Acute Inflammation Symptoms:
Acute inflammation typically shows these signs:
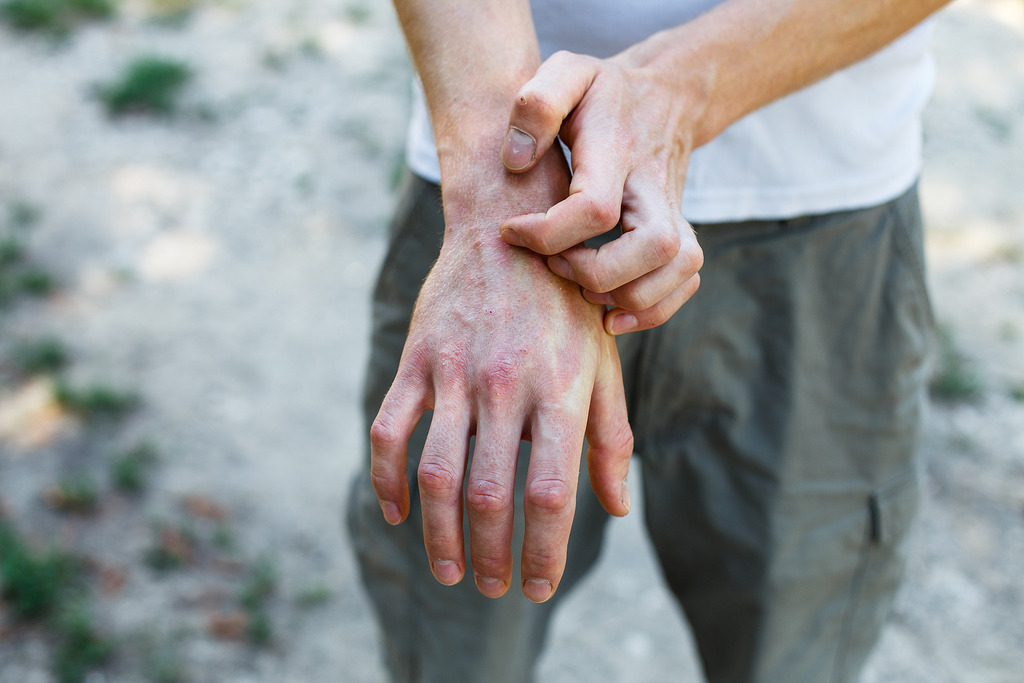
- Heat: The affected area feels warmer than usual.
- Pain: The area may be tender or painful.
- Redness: The skin around the affected area may appear red.
- Swelling: Fluid builds up around the affected area, causing it to swell.
- Loss of Function: The function of the affected area may be temporarily impaired.
Chronic Inflammation Symptoms:
Long-term inflammation can manifest in a variety of ways, including:
- Body aches and joint pain
- Constant fatigue and trouble sleeping
- Mood disorders like anxiety and depression
- Gastrointestinal issues, including bloating, constipation, and diarrhea
- Unexplained weight changes
- Frequent infections
In autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis , the immune system attacks the joints, leading to symptoms like joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.

Causes of Inflammation
Inflammation can result from several factors, including:
- Chronic conditions: Conditions like arthritis, diabetes, and obesity can lead to persistent inflammation.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections often trigger acute inflammation.
- Medications: Some medications can cause inflammation as a side effect.
- Diet: Certain foods, particularly those high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and trans fats, are known to contribute to chronic inflammation. Alcohol is also linked to inflammation.
How is Inflammation Diagnosed?
There is no single test to diagnose inflammation, but your doctor may use a combination of tests based on your symptoms.
Key Diagnostic Tests:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can reveal markers for inflammation, such as C-reactive protein ( CRP ) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate ( ESR ).
- Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP): This test measures protein levels in the blood and can help confirm chronic inflammation.
- Fibrinogen: High fibrinogen levels can indicate inflammation.
Imaging Tests:
If you are experiencing symptoms like chronic diarrhea or face numbness, imaging tests like colonoscopies or MRI may be used to visualize the inflammation in specific body parts.

Home Remedies to Reduce Inflammation
Anti-inflammatory Foods:
Your diet plays a major role in inflammation. Eating foods that fight inflammation can help improve your condition. Some of the most effective anti-inflammatory foods include:
- Berries and cherries
- Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel
- Green tea
- Broccoli and avocados
- Turmeric, ginger, and clove
You can also explore an anti-inflammatory diet for further benefits.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Engage in moderate exercise: Regular exercise can help manage inflammation, but be sure to balance with rest.
- Reduce stress: Chronic stress can worsen inflammation, so adopting stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga can help.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a major contributor to inflammation.
- Manage existing health conditions: Conditions like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease can exacerbate inflammation, so managing these through treatment and lifestyle changes is essential.

Other Treatments for Inflammation
If you are dealing with chronic inflammation or an autoimmune disease, several treatment options are available.
Over-the-Counter Medications:
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): These are commonly used to treat short-term inflammation and pain. Popular over-the-counter NSAIDs include ibuprofen (Advil) and naproxen (Aleve).
- Aspirin: Available over the counter, aspirin can also help with inflammation, but it may cause side effects if used long-term.
Prescription Medications:
- Corticosteroids: These are strong anti-inflammatory medications prescribed for severe inflammation. They can be taken orally, through injections, or as topical creams. Corticosteroids are typically used for autoimmune conditions and severe allergies.
Topical Treatments:
Topical analgesics and creams can provide localized relief from inflammation. Some creams contain NSAIDs like diclofenac , which can be helpful for joint inflammation in conditions like arthritis.
The Takeaway
Inflammation is a necessary and natural process that helps your body heal from injury and infection. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to health problems, particularly if it is related to an autoimmune disorder. Acute inflammation typically resolves on its own once the underlying cause is treated, but chronic inflammation may require medical intervention and lifestyle changes.
If you suspect you have chronic inflammation, it’s important to consult your doctor to identify the underlying cause and determine an appropriate treatment plan. With the right diagnosis and treatment, managing inflammation and reducing its harmful effects on your health is possible.