Understanding Heart Disease Risk
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S., accounting for 1 in 5 deaths in 2020 alone. Early screening and preventive measures can help reduce the risk and allow for timely intervention.
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends starting routine heart health screenings at age 20, with follow-up screenings based on:
- Test results
- Personal health status
- Family history
The primary goal of screening is early identification of risk factors to take preventive measures and avoid severe complications.
Routine Heart Health Screenings
Medical History Evaluation
Your doctor will inquire about your lifestyle, including:
- Physical activity levels
- Dietary habits
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Personal and family medical history
Physical Examination
Doctors assess blood pressure, weight, BMI (Body Mass Index), and waist circumference to evaluate heart disease risk.
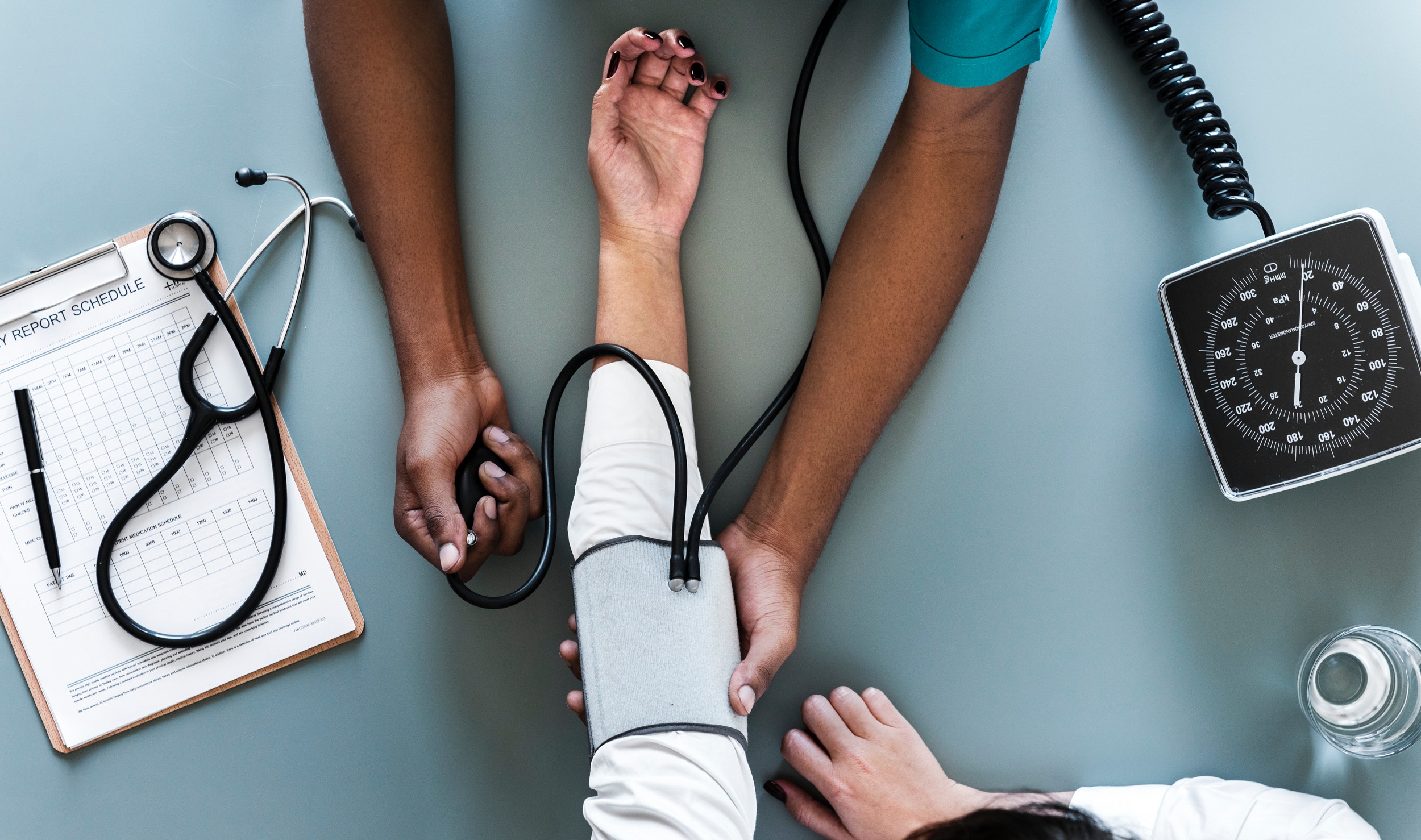
Blood Pressure Monitoring
Hypertension ( high blood pressure research ) is a major risk factor for heart disease. Regular monitoring can help detect issues early.
| Blood Pressure Category | Systolic (mm Hg) | Diastolic (mm Hg) |
| Normal | < 120 | < 80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 | < 80 |
| High Blood Pressure – Stage 1 | 130-139 | 80-89 |
| High Blood Pressure – Stage 2 | ≥140 | ≥90 |
| Hypertensive Crisis | ≥180 | ≥120 |
Note: A reading of 180/120 mm Hg or higher requires immediate medical attention.
BMI and Waist Circumference
- BMI Categories:
- Normal: 18.5-24.9
- Overweight: 25.0-29.9
- Obesity: ≥30.0
- Healthy Waist Circumference:
- Men: < 40 inches
- Women (non-pregnant): < 35 inches
A high waist circumference is associated with fat accumulation in the liver, increasing the risk of liver disease and heart disease ( research link ).
Blood Tests
Cholesterol Testing
Excess cholesterol can lead to artery blockages, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes ( cholesterol testing ). A simple blood test measures:
- HDL (good cholesterol)
- LDL (bad cholesterol)
- Triglycerides
It is recommended to check cholesterol levels every 4-6 years. If you are at higher risk for heart disease, more frequent testing may be necessary.
Blood Sugar Testing
High blood sugar levels can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, both of which contribute to heart disease ( blood sugar testing ).
| Test Type | A1C (%) | Fasting Blood Sugar (mg/dL) | Glucose Tolerance (mg/dL) |
| Normal | < 5.7 | ≤ 99 | ≤ 140 |
| Prediabetes | 5.7 – 6.4 | 100 – 125 | 140 – 199 |
| Diabetes | ≥ 6.5 | ≥ 126 | ≥ 200 |
Recommendation: Screen every 3 years from age 45; earlier and more frequent testing may be needed for high-risk individuals.
Additional Testing
If routine tests indicate early signs of heart disease, your doctor may recommend further heart monitoring or imaging to assess your condition.
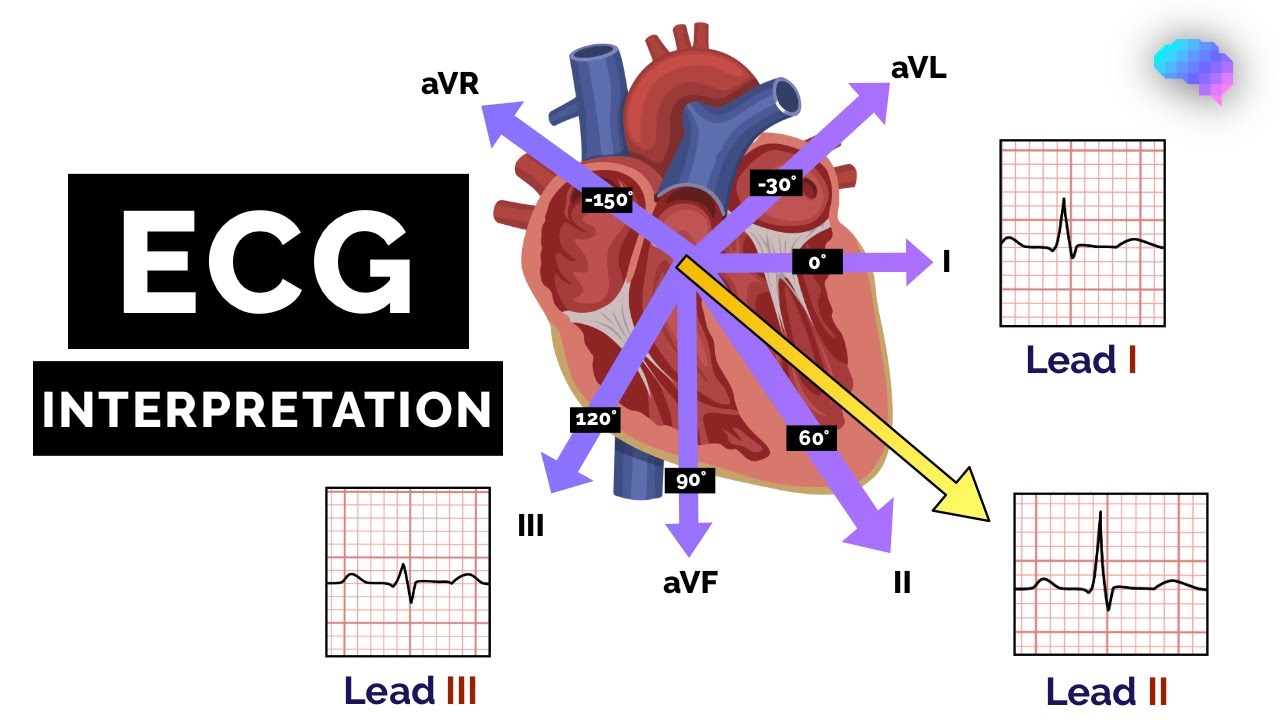
Heart Monitoring
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
- Detects irregular heart rhythms
- Uses electrode patches to monitor heart activity
- Holter Monitor
- A portable ECG device worn for 24-48 hours or longer
- Records heart activity in different settings
- Stress Test
- Evaluates heart function under physical or medication-induced stress
Heart Imaging
- Echocardiogram (ECHO): Uses ultrasound to assess heart structure and function
- CT/MRI scans: Provide detailed imaging of the heart and blood vessels
- Coronary Angiography ( related study ): Examines blood flow to the heart and may require catheter-based evaluation
Genetic Testing
Some forms of heart disease have a genetic component ( genetic testing ). If you have a first-degree relative diagnosed with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM), consult your doctor about genetic screening.
Conclusion
Heart disease can be prevented and managed through regular testing and healthy lifestyle choices. Recommendations:
- Start screenings at age 20
- Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar, BMI, and waist circumference
- Discuss additional testing with your doctor if you have a family history or other high-risk factors
Take proactive steps to protect your heart health!