1. Overview of Pregnancy Varicose Veins
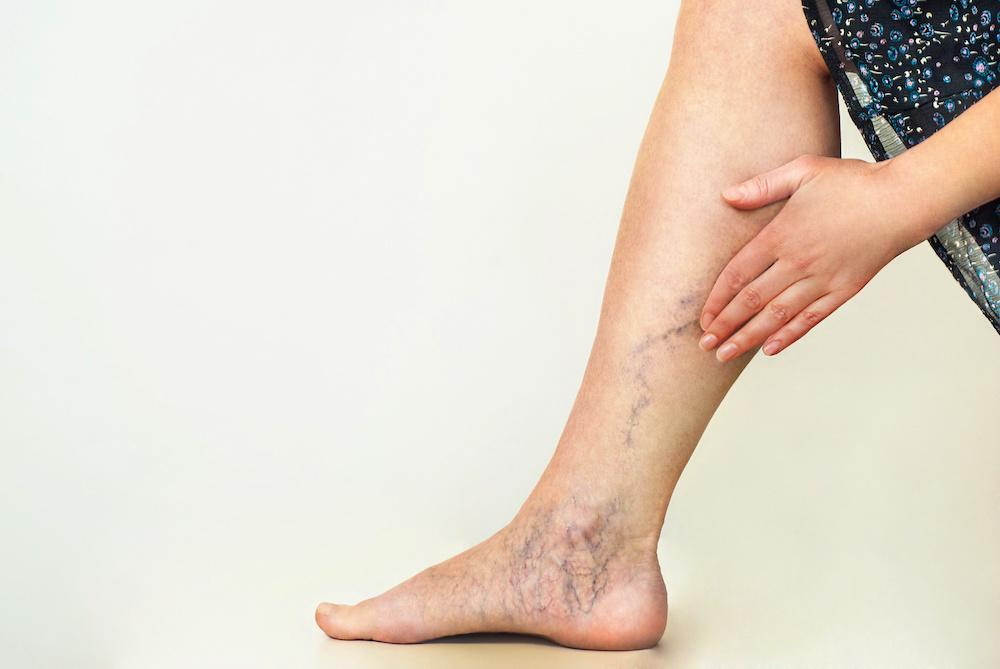
During pregnancy, many women notice that their legs exhibit visibly enlarged and twisted superficial veins, commonly known as varicose veins. This condition is largely caused by the growing uterus exerting pressure on the circulatory system, which disrupts the normal return of blood from the legs to the heart. Although typically harmless, the discomfort associated with varicose veins warrants attention.
2. Causes of Varicose Veins During Pregnancy
- Increased Blood Volume
During pregnancy, the body’s blood volume can increase by about 20%. With the number of veins remaining constant, each vessel must work harder to transport the extra blood, resulting in increased pressure on the veins. - Hormonal Changes
Elevated hormone levels, especially progesterone, relax the muscles in the vein walls and the ligaments in the pelvis. This relaxation hampers the veins’ ability to efficiently pump blood upward, leading to dilation and impaired valve function. - Genetic Factors
A family history of varicose veins can increase the likelihood of developing this condition during pregnancy.
3. Symptoms and Potential Complications
Common symptoms of pregnancy-related varicose veins include:
- Mild swelling in the feet and ankles
- Aches, throbbing, or cramping sensations in the legs
- A feeling of heaviness in the lower limbs
- Noticeable blue or purple twisted veins on the legs
While these symptoms are often more cosmetic than harmful, a rare progression to venous insufficiency can occur, potentially leading to skin breakdown, inflammation, and even blood clots. If you experience significant skin changes, severe pain, or bleeding, seek medical advice immediately.
4. Treatment and Management Strategies
4.1 Conservative Treatments
- Compression Therapy
Wearing compression stockings is a common and effective way to manage varicose veins during pregnancy. These stockings, available in various pressure levels (typically recommended between 20-30 mmHg), help improve blood circulation and alleviate discomfort. Options with lower pressures (8-15 mmHg) are also available under a doctor’s guidance. - Lifestyle Adjustments
Simple changes in daily habits can help relieve vein pressure, including: - Elevating your legs frequently to reduce blood pooling.
- Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as walking or swimming, after consulting with your doctor.
- Avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting by taking regular breaks to move around.
- Keeping your legs uncrossed while sitting to prevent additional pressure on your veins.
- Sleeping on your left side to minimize pressure on the inferior vena cava.
4.2 Medication and Warnings
Some expectant mothers may consider using horse chestnut extract to alleviate symptoms. However, caution is advised because consuming any unprocessed parts of the horse chestnut plant (such as its flowers, bark, leaves, or seeds) is toxic. Even with processing, the safety of horse chestnut extract during pregnancy or breastfeeding remains uncertain. Medical professionals typically discourage elective procedures to remove varicose veins during pregnancy, as symptoms usually subside after childbirth.

5. Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments
To minimize discomfort and prevent varicose veins from worsening, consider the following measures:
- Daily Care
- Regularly elevate your legs to reduce blood pooling.
- Maintain a consistent routine of low-intensity exercise.
- Take breaks to move around if you must sit or stand for long periods.
- Wear comfortable, supportive maternity garments, especially stockings designed for leg support.
- Dietary Adjustments
- Reduce salt intake to prevent excessive swelling.
- Stay well-hydrated and consume a fiber-rich diet to prevent constipation.
- Footwear Choices
- Avoid high heels and opt for flat or low-heeled shoes, which can help stimulate calf muscles and promote better circulation.
6. The Connection Between Varicose Veins and Hemorrhoids
It is important to note that hemorrhoids share a similar origin with varicose veins, as both are caused by swollen, twisted veins. In pregnancy, increased abdominal pressure and straining during delivery can exacerbate hemorrhoids, leading to symptoms such as swelling, bleeding, and pain around the anal area. If these symptoms become severe, consult your healthcare provider.
7. Postpartum Recovery and Considerations
For most women, varicose veins that develop during pregnancy gradually improve within about three months after giving birth. Even if the veins do not completely disappear, the discomfort and prominence usually decrease significantly. However, if you experience persistent pain, redness, swelling, or any signs of skin deterioration or bleeding, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
This article is designed to provide expectant mothers with comprehensive knowledge and practical advice for managing varicose veins during pregnancy. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized medical guidance.