What is Gigantism?
Gigantism is a rare condition that results in abnormal growth in children, particularly in terms of height and body size. It occurs when the child’s pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone, also known as somatotropin. Early diagnosis is crucial, as prompt treatment can stop or slow down the excessive growth and prevent the child from growing abnormally large. However, gigantism can sometimes be difficult for parents to detect as its symptoms may initially resemble normal childhood growth spurts.
What Causes Gigantism?
In most cases, gigantism is caused by a tumor on the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain and about the size of a pea, produces hormones that regulate many bodily functions, including:
- Temperature control
- Sexual development
- Growth
- Metabolism
- Urine production
When a tumor grows on the pituitary gland, it causes the gland to produce more growth hormone than the body requires.
In addition to tumors, other less common causes of gigantism include:
- McCune-Albright syndrome: A genetic condition that causes abnormal bone growth, patches of light-brown skin, and glandular abnormalities.
- Carney complex: An inherited condition that leads to non-cancerous tumors in connective tissues, as well as cancerous or non-cancerous tumors in endocrine glands and darkened skin spots.
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1): A hereditary disorder that leads to tumors in the pituitary, pancreas, or parathyroid glands.
- Neurofibromatosis: A genetic disorder that causes tumors to form in the nervous system.

Recognizing the Symptoms of Gigantism
If your child has gigantism, you may notice they are much larger than other children their age. Some parts of their body may also appear disproportionately larger than others. Common symptoms include:
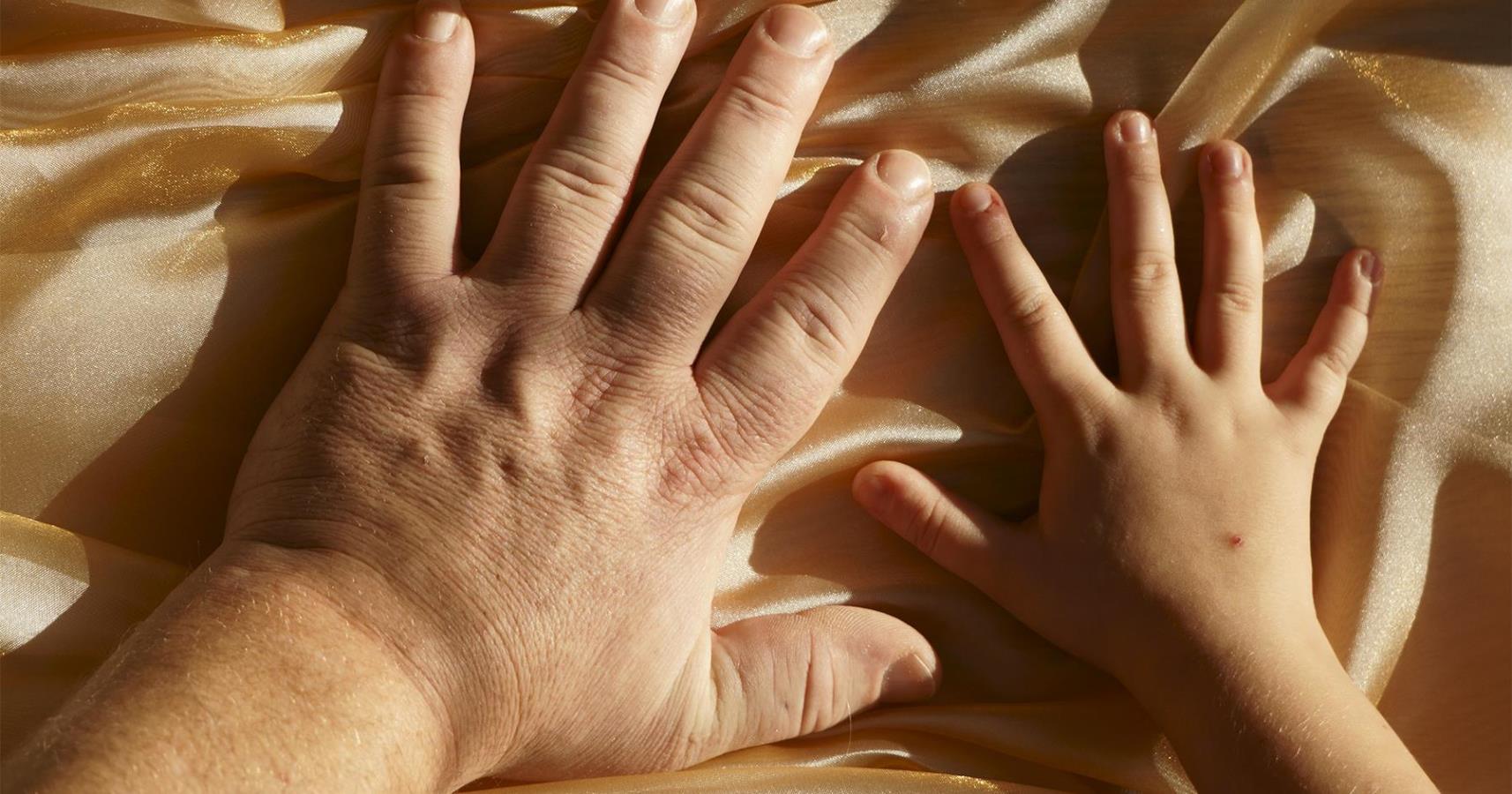
- Very large hands and feet
- Thick toes and fingers
- Prominent jaw and forehead
- Coarse facial features
Children with gigantism may also have flat noses, large heads, lips, or tongues.
The severity of symptoms depends on the size of the pituitary tumor. As the tumor grows, it can press on nerves in the brain, causing headaches, vision problems, or nausea. Additional symptoms of gigantism may include:
- Excessive sweating
- Severe or recurrent headaches
- Weakness
- Insomnia and other sleep disorders
- Delayed puberty in both boys and girls
- Irregular menstrual periods in girls
- Deafness
How is Gigantism Diagnosed?
If your child’s doctor suspects gigantism, they may recommend blood tests to measure growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels. IGF-1 is a hormone produced by the liver. The doctor may also recommend an oral glucose tolerance test.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
In this test, your child will drink a special beverage containing glucose, a form of sugar. Blood samples will be taken before and after drinking the beverage. In a normal body, growth hormone levels decrease after consuming glucose. If your child’s levels remain elevated, it indicates that their body is producing too much growth hormone.
If blood tests suggest gigantism, your child will need an MRI scan of the pituitary gland to detect the tumor and assess its size and position.
How is Gigantism Treated?
The treatment for gigantism focuses on reducing or stopping the overproduction of growth hormone.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the tumor is the preferred treatment for gigantism if it is the underlying cause. The surgeon will access the tumor by making an incision through the nose. Microscopes or small cameras may be used to assist in viewing the tumor within the gland. In most cases, your child should be able to return home the day after the surgery.
Medication
If surgery is not an option—such as when there is a high risk of damaging critical blood vessels or nerves—medications may be prescribed. These medications aim to shrink the tumor or reduce the production of excess growth hormone.
Common medications include:
- Octreotide or Lanreotide: These medications mimic another hormone that inhibits growth hormone production and are usually injected once a month.
- Bromocriptine and Cabergoline: These drugs lower growth hormone levels and are typically taken in pill form, often in combination with octreotide.
- Pegvisomant: If other drugs are not effective, daily injections of pegvisomant may be used. This medication blocks the effects of growth hormones and lowers IGF-1 levels in your child’s body.
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
Gamma knife radiosurgery is an option if traditional surgery is not possible. The “gamma knife” is a collection of highly focused radiation beams that deliver powerful radiation precisely to the tumor. This treatment does not damage surrounding tissue but can destroy the tumor. Gamma knife treatment may take months or even years to be fully effective in normalizing growth hormone levels.
However, due to the association of this type of radiation with obesity, learning disabilities, and emotional issues in children, it is typically only used when other treatment options fail.
Long-Term Outlook for Children with Gigantism
According to St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center, 80% of gigantism cases caused by the most common type of pituitary tumor are cured with surgery. If the tumor recurs or surgery cannot be performed safely, medications can be used to reduce symptoms and help the child lead a long and fulfilling life. Learn more here .