Overview of Lupus and Skin Issues
Lupus is not only a systemic autoimmune disease but also frequently presents with skin abnormalities. Some patients may experience only cutaneous lupus without systemic involvement. Regardless of the type, skin issues significantly impact quality of life, making early recognition and treatment essential.
Skin Manifestations and Common Symptoms
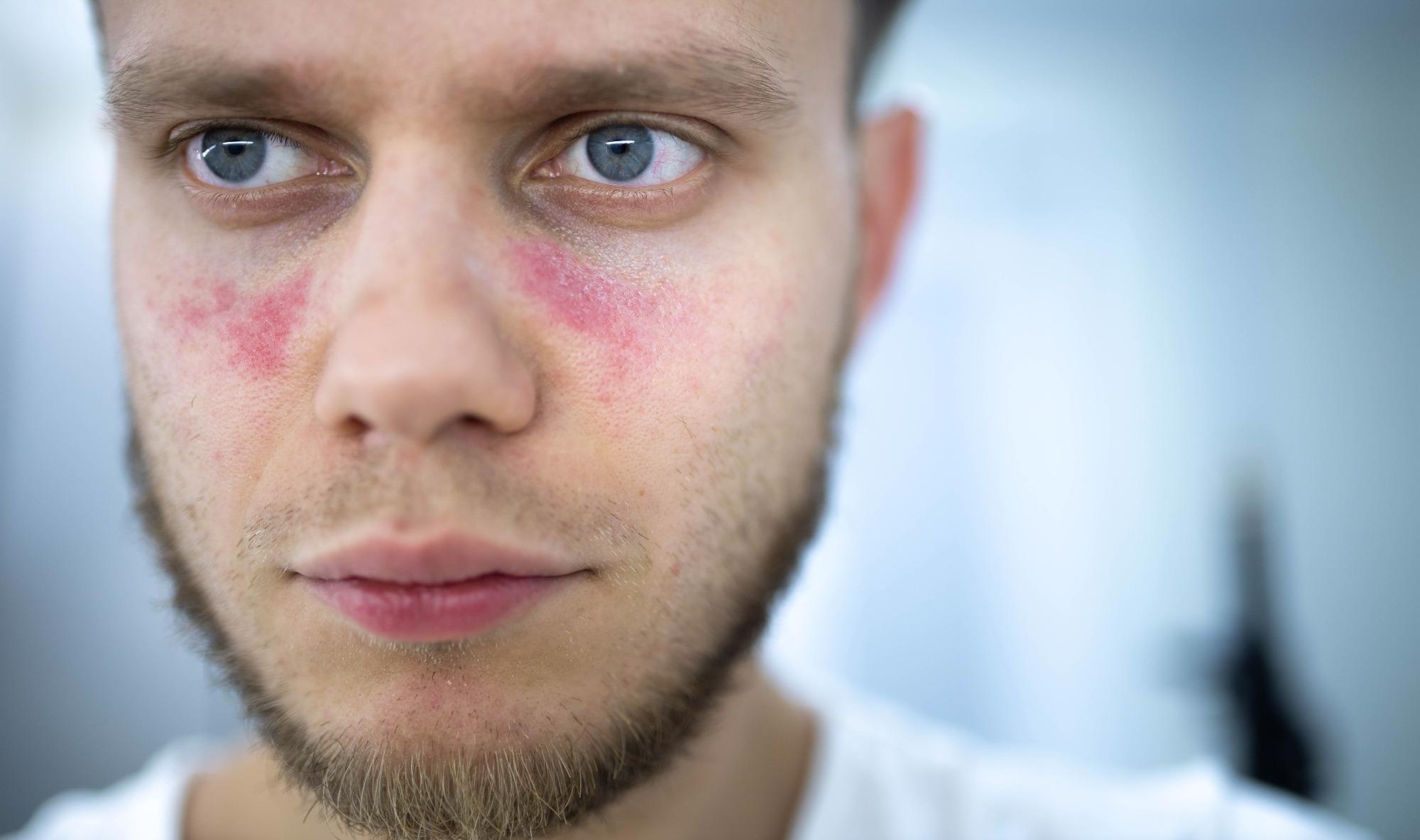
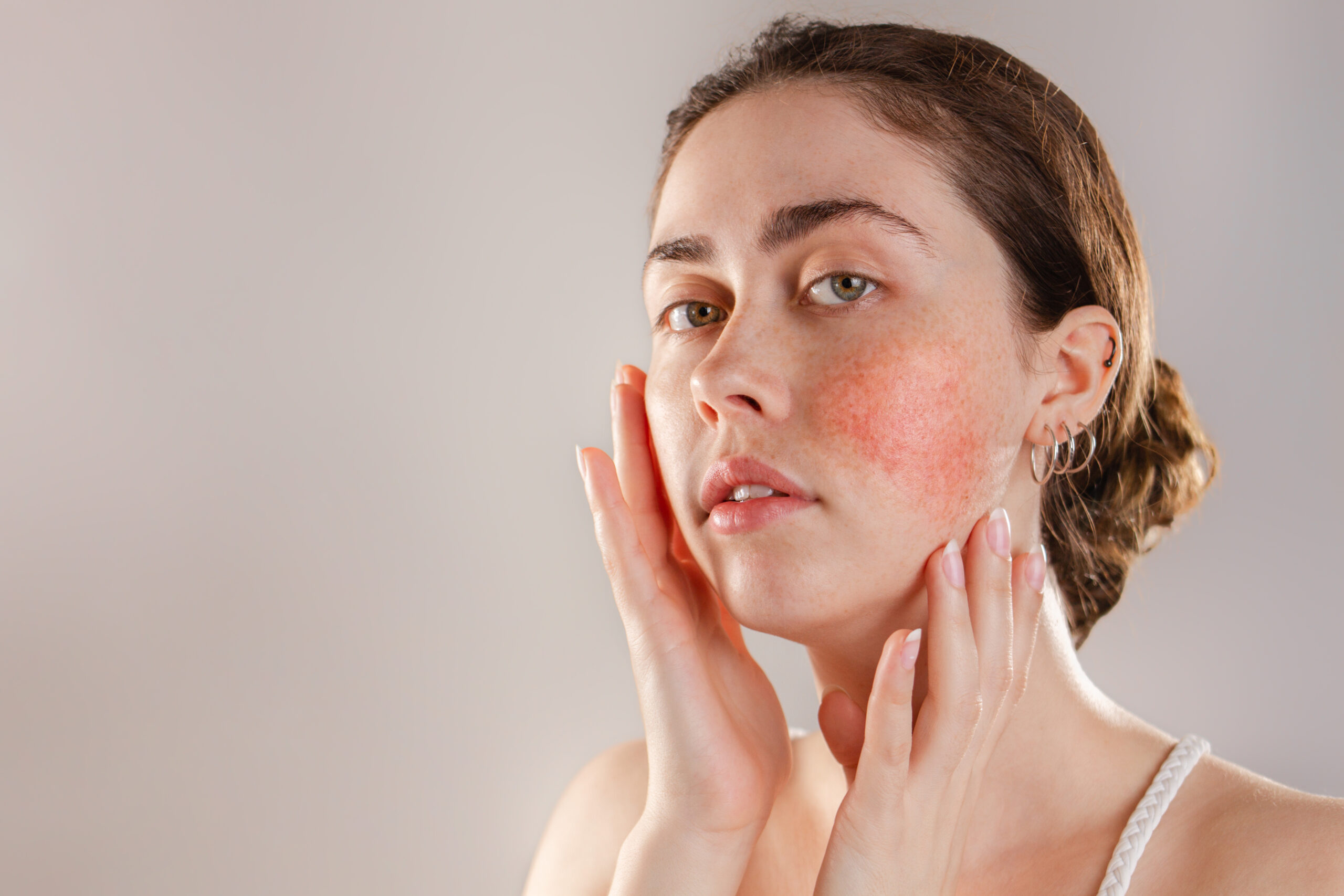
Malar Rash
- Appearance: Typically presents as a butterfly-shaped rash across the nose and cheeks, ranging from mild redness to noticeable scaling.
- Triggers: Ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight can worsen the condition, intensifying the rash.
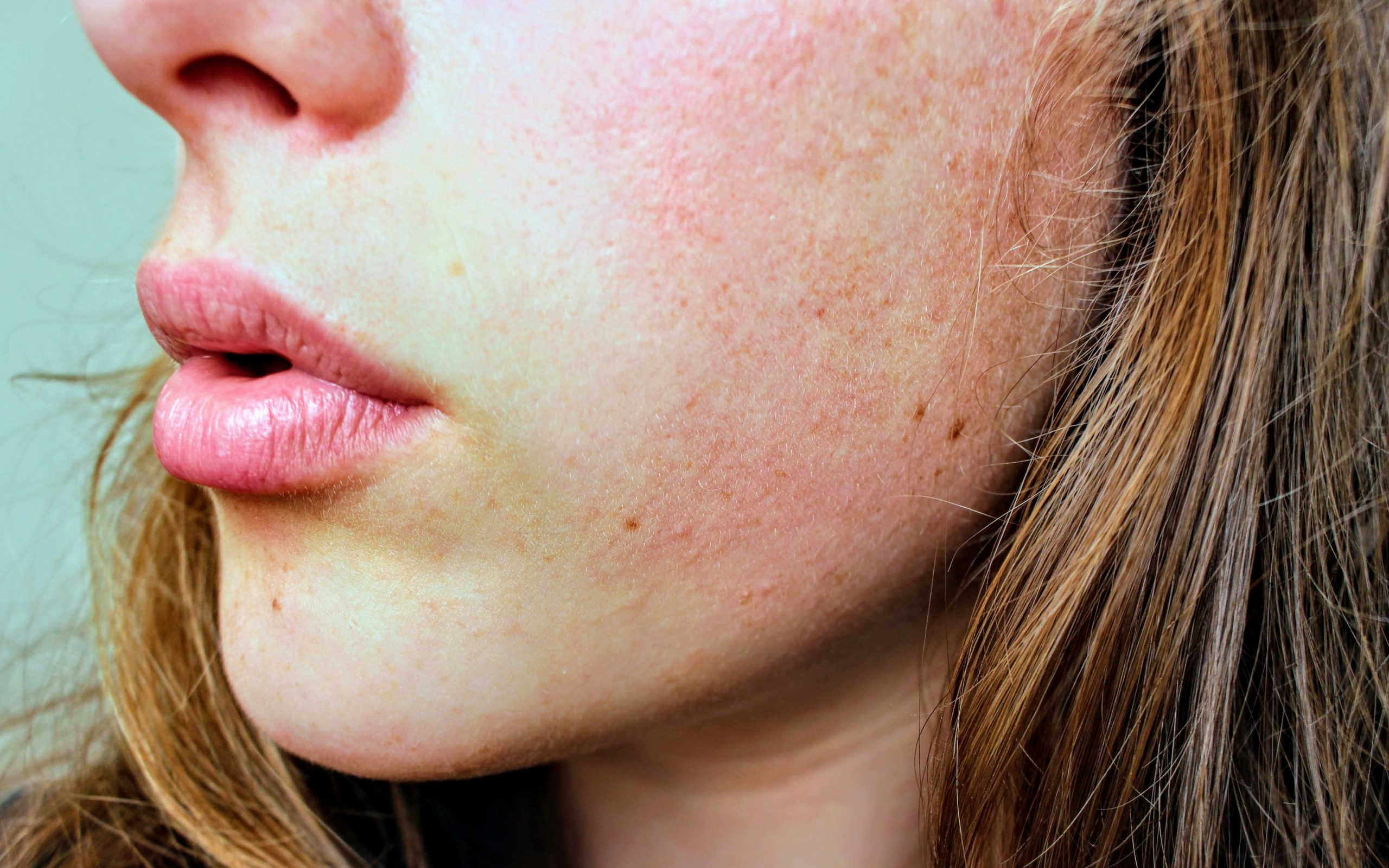
Subacute Cutaneous Lesions
- Characteristics: Primarily triggered by UV exposure, these appear as red, scaly, or annular patches, often on exposed areas like the arms, shoulders, and neck.
- Effects: While scarring is rare, these lesions may lead to localized hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
Discoid Rash and Mucosal Damage
- Appearance: Patients may develop round or coin-shaped ulcers in the mouth, nasal cavity, or genital areas. These painful ulcers often leave scars, and scalp involvement can cause permanent hair loss.
Other Skin Abnormalities
- Hair Issues: Some patients experience hair loss or brittle hair, likely due to the immune system attacking hair follicles.
- Vasculitis: Damage to skin blood vessels may result in purplish-red spots or larger nodules, attributed to cutaneous vasculitis.
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Fingertips or toes may turn red, white, or blue in cold conditions, accompanied by numbness or tingling.
- Livedo Reticularis: A net-like, purplish pattern may appear on the skin, especially on the lower limbs, worsening in cold weather.
For more details on symptoms and risk factors, refer to this Lupus Symptoms and Risk Factors guide.
Treatment Options Explained
Topical Treatments
- Local Steroids: Commonly used medications include steroid creams or gels, effective for mild to moderate skin lesions. For larger inflamed areas, steroid injections may be administered for faster relief.
- Over-the-Counter Products: Mild rashes can be managed with low-potency steroids like hydrocortisone cream to reduce inflammation.
Systemic Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Drugs like ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin help relieve systemic inflammation and pain. Learn more about NSAIDs.
- Oral Steroids: Used for widespread rashes, but side effects limit long-term use.
- Antimalarial Drugs: Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) and chloroquine regulate the immune system to improve skin inflammation. High doses over time may affect eye health, requiring regular eye exams.
Local Immunomodulators
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Tacrolimus ointment and pimecrolimus cream effectively control localized inflammation, serving as alternatives to traditional steroids.
Prevention and Daily Care
Strict Sun Protection
- Measures:
- Avoid outdoor activities between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. to minimize UV exposure.
- Wear long-sleeved clothing, pants, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses.
- Apply broad-spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, reapplying every two to four hours, especially after sweating or swimming.
For detailed advice, check out this Sun Protection Guide.
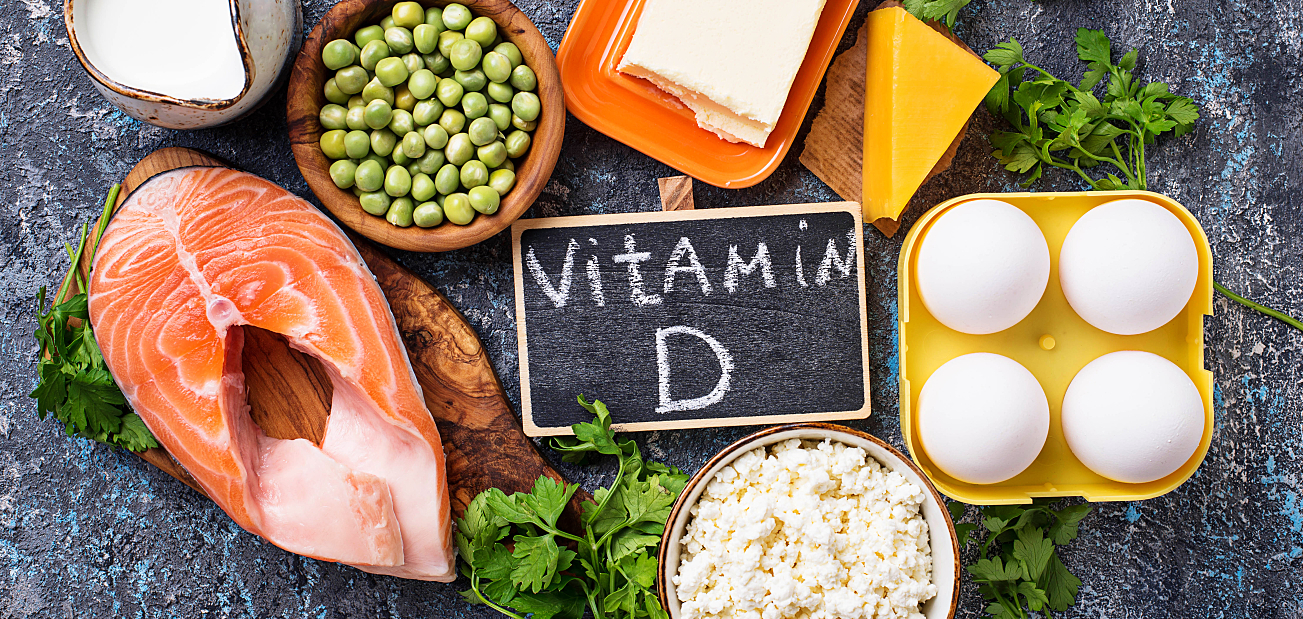
Vitamin D Supplementation
Prolonged sun avoidance may lead to vitamin D deficiency. Blood tests can confirm levels, and supplementation should be guided by a doctor.

Smoking Cessation and Healthy Habits
- Quit Smoking: Smoking worsens lupus symptoms and may reduce the effectiveness of drugs like hydroxychloroquine.
- Skin Care: Avoid scratching or self-treating lesions to prevent infections or scarring.
- Warmth: For those prone to Raynaud’s, keeping hands and feet warm with gloves or socks is crucial.
Summary and FAQs
Summary
Lupus affects more than just internal systems; its diverse skin manifestations—from malar rash to ulcers and hair loss—require attention. Through targeted topical and systemic treatments, combined with preventive steps like sun protection and smoking cessation, skin symptoms can be managed effectively, enhancing quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the skin manifestations of lupus?
Primarily a butterfly-shaped rash across the nose and cheeks, along with red, scaly, or annular patches. - How does lupus alter facial appearance?
Beyond the malar rash, it may cause facial swelling, abnormal pigmentation, or localized scarring. - Does the disease affect overall appearance?
Yes, chronic inflammation can lead to hair loss, rough skin, and nail changes, altering one’s look. - Can lupus change skin tone?
Yes, subacute lesions often cause hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation in affected areas.