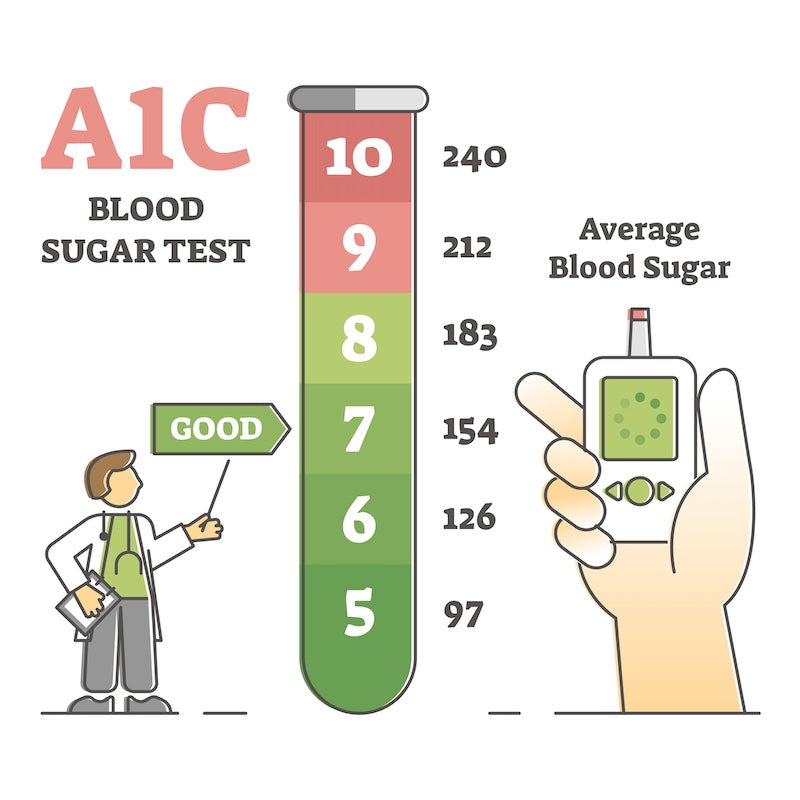
Diabetes management relies on regularly checking your blood sugar levels. Doctors often recommend an A1c blood test every few months to measure the average blood sugar over the past two to three months. The goal is typically to keep the A1c level below 7% to minimize complications.
1. Understanding A1c Testing
Unlike daily blood sugar checks, the A1c test measures the percentage of sugar that binds with hemoglobin in red blood cells over a period of two to three months. Maintaining an A1c level below 7% can significantly reduce the risk of complications affecting the eyes, nerves, and cardiovascular system.
2. Planning a Balanced Diet
a. Control Your Portions
Using kitchen tools such as measuring cups and food scales can help you accurately manage portion sizes. Overeating, especially foods high in carbohydrates, can spike your blood sugar levels.
b. Choose Quality Carbohydrates
Opt for whole grains, vegetables, and fruits that are high in dietary fiber to slow down sugar absorption. For further guidance on healthy eating for diabetes, explore the healthy eating guidelines provided by the American Diabetes Association. Adopting a Mediterranean diet is another effective strategy to promote steady blood sugar levels and support heart health.
c. Plan Your Plate
An ideal plate should be divided into portions with half of the plate filled with non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein (such as insulin-friendly options), and one-quarter with whole grains. A well-planned meal can help avoid drastic blood sugar fluctuations.
3. Weight Management and Exercise
a. Achieve a Healthy Weight
For individuals who are overweight, losing just 5%–10% of your body weight can improve insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to use sugar more efficiently and lower your A1c levels.
b. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Combine aerobic exercise with resistance training to enhance the muscles’ ability to absorb glucose. The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week. This regular physical activity not only improves blood sugar control but also contributes to overall health.

4. Follow Your Doctor’s Advice
Even with proper diet and exercise, taking your diabetes medication on schedule is essential. Whether it’s injectable insulin or oral medications, adherence to your prescribed regimen is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and achieving target A1c results.
5. Wisely Use Supplements
Some supplements—such as berberine, CoQ10, or cinnamon—may support blood sugar control. However, always consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen to ensure they won’t interfere with your current medications.
6. Consistency and Regular Follow-Up
Because the A1c test reflects long-term blood sugar control, it is important to maintain healthy lifestyle changes consistently. Regular testing (typically every three months) will help you monitor progress and adjust your plan as needed.
By optimizing your dietary control, engaging in regular exercise, managing your weight, strictly following your prescribed medication plan, and using supplements appropriately, you can gradually lower your A1c level and achieve better overall diabetes management. The key is a comprehensive, sustained approach that not only protects your health but also helps prevent complications.
We hope this guide provides you with practical tips to take control of your diabetes journey and lead a healthier life!