Systemic Health Threats
Poor blood glucose control over time can lead to dysfunction in multiple organ systems. This section provides an in-depth analysis of the nine major complications associated with diabetes and their management strategies, aiming to assist patients in developing a scientific health management plan.
Cardiovascular System Protection
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality among diabetic patients. It is recommended that patients regularly undergo the following tests:
- Dynamic Blood Pressure Monitoring: Use an arm-type blood pressure monitor to track arterial blood flow status.
- Lipid Profile Testing: Focus on monitoring low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Baseline Electrocardiogram Screening: Establish a record of cardiac electrical activity.
Patients with a history of smoking or a family history of cardiovascular diseases should develop a comprehensive prevention plan that includes weight management, regular exercise, and psychological adjustment, aiming to maintain blood pressure within the ideal range of <130/80 mmHg.
Stroke Warning Signs
Sudden onset of facial or limb numbness, speech difficulties, blurred vision, or dizziness may be stroke warning signs. Immediate medical attention is crucial. Neurologists will perform neurological examinations and imaging studies for diagnosis.
Kidney Function Monitoring
Annual urine microalbumin tests are essential for screening diabetic nephropathy, alongside serum creatinine tests to assess glomerular filtration rate. Patients with hypertension or cardiovascular diseases should have more frequent screenings and strictly control protein intake.
Neuropathy Management
Distal symmetric neuropathy presents as burning pain or numbness in the hands and feet. Recommendations include:
- Daily self-examination of limb skin condition.
- Annual 10g monofilament testing.
- Timely treatment of foot calluses.
Patients diagnosed with peripheral neuropathy should receive professional foot care guidance to prevent diabetic foot ulcers.
Visual System Protection Plan
All diabetic patients should have annual eye examinations, including:
- Pupil dilation retinal imaging.
- Intraocular pressure measurement.
- Visual field assessment.
Pregnant women with gestational diabetes should undergo comprehensive retinal examinations in early pregnancy. Patients with type 1 diabetes should begin annual screenings 3-5 years after diagnosis.
Gastrointestinal Function Regulation
Gastroparesis patients can be evaluated using gastric emptying scintigraphy or smart pill monitoring. Dietary modifications and prokinetic medications can effectively alleviate symptoms.
Metabolic Monitoring Techniques
- Glycated Hemoglobin Testing: Monitor quarterly until blood glucose is stable, then semi-annually.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems: Use subcutaneous sensors for ongoing glucose tracking.
- Urine Ketone Testing: Test when blood glucose exceeds 240 mg/dL or when experiencing polyuria and polydipsia.
Endocrine System Comorbidities
The American Diabetes Association recommends that patients with type 1 diabetes regularly screen for hypothyroidism, especially women over 40 or those with a family history of thyroid disorders, with tests every 1-2 years.
Infection Prevention
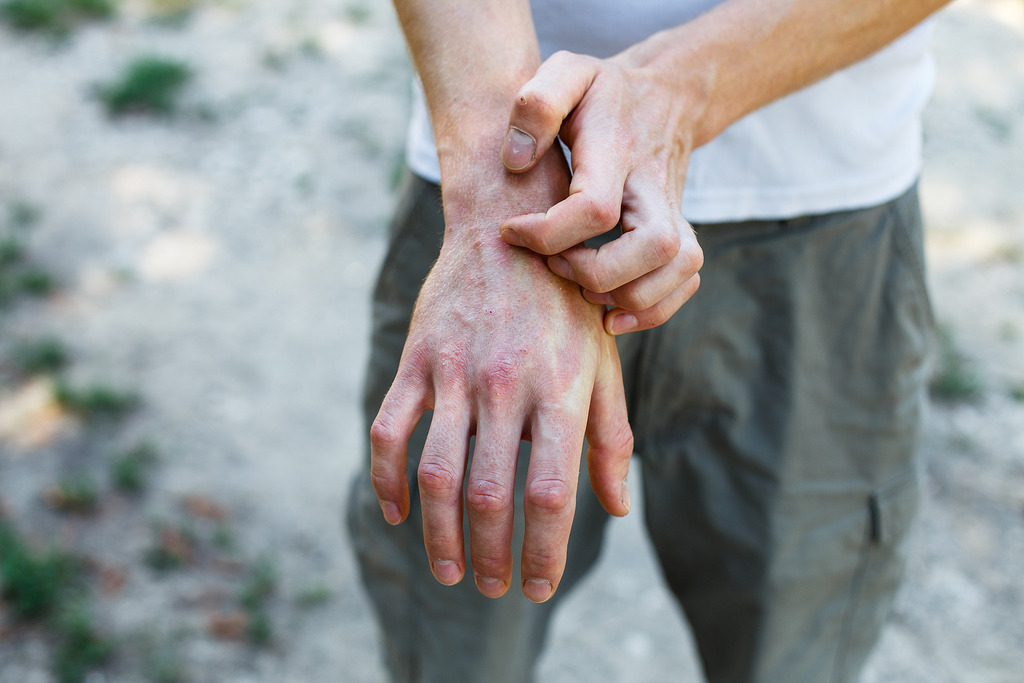
Hyperglycemia increases the risk of urinary tract, periodontal, and skin infections. Preventive measures include:
- Daily oral hygiene using antimicrobial mouthwash.
- Regular dental cleanings to prevent periodontal disease.
- Prompt care of minor skin injuries.
Sexual Function Maintenance
Male patients experiencing erectile dysfunction should consider vacuum erection devices or PDE5 inhibitors, while also evaluating cardiovascular risk factors.
Comprehensive Health Management
Establish a personalized prevention system that includes:
- Quarterly metabolic indicator monitoring.
- Annual organ function assessments.
- Customized exercise plans.
- Dietary guidance from nutritionists.
- Psychological support interventions.
Through early screening and standardized management, diabetic patients can delay the progression of complications and maintain a high quality of life. Collaborating with healthcare providers to develop a tailored examination schedule is highly recommended.