chizophrenia is a complex mental health disorder characterized by, among other symptoms, vivid auditory hallucinations—commonly referred to as “hearing voices.” These hallucinations can make patients feel as though they are in constant conversation with an unseen “interlocutor,” disrupting their thoughts and emotions. While some individuals may adapt to this phenomenon over time, many continue to experience persistent auditory hallucinations that significantly impair their quality of life. This article provides a comprehensive overview of various treatment methods and self-regulation strategies to help manage auditory hallucinations, offering practical guidance for patients and their families.
Background on Auditory Hallucinations
Up to 80% of individuals with schizophrenia experience auditory hallucinations, a phenomenon medically termed auditory verbal hallucinations. Patients may perceive “voices” that are critical, threatening, or even command them to harm themselves or others. Given the complexity and variability of these symptoms, many patients face long-term challenges in managing them.
Treatment Approaches
To help patients cope with auditory hallucinations, healthcare professionals have developed several treatment options. Below are some of the primary methods:
1. Medication
Commonly prescribed antipsychotic medications can effectively reduce the intensity and frequency of hallucinations, making them less intrusive.
- Mechanism of Action: These medications help decrease the patient’s urge to engage with the hallucinations and reduce the perceived threat.
- Individual Variability: Responses to medication vary, so it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to adjust dosages or switch medications as needed, allowing sufficient time to observe effects.
2. Psychological Therapies
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Through cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), patients can learn to understand and reframe the negative emotions associated with hallucinations. This therapy helps patients:
- Reduce anxiety caused by hallucinations;
- Enhance self-control;
- Improve self-awareness, minimizing the disruption of daily life.
Telehealth
For patients with mobility issues or those living in remote areas, telehealth offers a convenient way to access professional psychological support from home.
Avatar Therapy
An emerging treatment, avatar therapy, uses computer technology to create a virtual representation of the hallucinated voice. By interacting with this avatar, patients learn to confront and control their hallucinations. Typically conducted over six weeks with weekly 30-minute sessions, preliminary studies suggest this method can reduce the frequency and emotional impact of hallucinations, though further research is needed to confirm its long-term efficacy.
3. Support Groups
Joining support groups allows patients to share experiences and strategies with others facing similar challenges. Organizations like NAMI provide valuable resources and educational services.
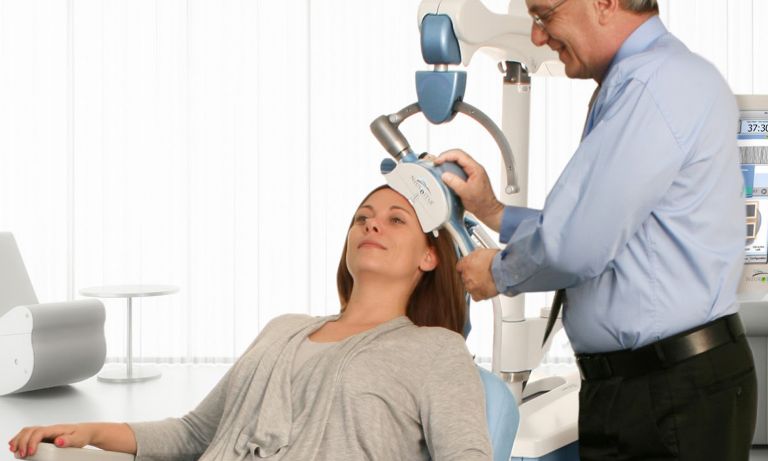
4. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (RTMS)
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (RTMS) is a non-invasive neurostimulation technique that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific brain regions, potentially reducing the intensity and frequency of hallucinations. While the exact mechanisms remain unclear, some studies have shown that patients experience symptom relief for several months following RTMS treatment.
Self-Regulation Strategies
In addition to professional treatment, patients can employ the following strategies to manage and alleviate the distress caused by auditory hallucinations:
- Distraction Techniques: Engage in activities like puzzles, reading, listening to music, watching TV, or household chores to divert attention from the hallucinations.
- Verbal Expression: Reading aloud, singing, or talking to oneself can help diminish the impact of hallucinations.
- Journaling: Keeping a detailed record of when and where hallucinations occur, along with potential triggers, can help identify patterns and provide valuable information for healthcare providers.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Drugs: These substances can exacerbate hallucinations and interfere with medication efficacy.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and mindful breathing can help reduce stress and improve emotional well-being.
- Assertive Responses: When hallucinations become overwhelming, patients can practice assertive responses, such as saying, “I’m not available to talk right now,” to regain a sense of control.
Conclusion
While auditory hallucinations are a challenging and common symptom of schizophrenia, a combination of medication, psychological interventions, and self-regulation strategies can help patients manage this phenomenon and improve their quality of life. If hallucinations become severe or pose a risk, seeking immediate medical assistance is crucial. Healthcare professionals and support groups are invaluable allies in the journey toward better mental health.