Introduction
As we age, maintaining good hearing health becomes increasingly important. While many people may not notice hearing issues in their daily lives, scientific testing can help identify problems early, allowing for timely intervention. Regular hearing tests not only assess current hearing status but also provide crucial references for future health management.
Why is a Hearing Test Necessary?
Some individuals may believe their hearing is fine, but hearing loss often develops gradually, making early signs easy to overlook. Doctors recommend:
- Age-related changes: Approximately 14% of people aged 45-64 experience some degree of hearing loss, and this percentage rises to over 30% for those aged 65 and above.
- Prevention and early detection: It is recommended to have a hearing test every 10 years before the age of 50 and every 3 years after 50. Regular check-ups can help detect hearing abnormalities caused by work, lifestyle, or other factors.
The Hearing Test Process
The entire test takes about 30 minutes and is painless:
- Testing equipment: You will wear specialized headphones to test each ear separately. The doctor will play short tones of varying pitches and volumes to assess your perception of high and low frequencies, as well as loud and soft sounds.
- Speech test: In some parts of the test, you will hear spoken words and be asked to repeat them. This test is usually conducted in a soundproof environment to eliminate external interference and ensure accurate results.
- Test items: The test not only evaluates your hearing ability but also provides the doctor with detailed information about any asymmetry between your ears.
Interpreting Test Results
A hearing test is not a simple “pass” or “fail” check. Instead, it measures hearing ability at different decibel levels to determine the degree of hearing loss:
- Decibel standards:
- Normal hearing: Loss of 25 decibels or less
- Mild hearing loss: 26-40 decibels
- Moderate hearing loss: 41-55 decibels
- Moderately severe hearing loss: 56-70 decibels
- Severe hearing loss: 71-90 decibels
- Profound hearing loss: 91-100 decibels
- Significance: Even if you believe your hearing is fine, the test may reveal mild to moderate hearing loss. Early detection allows for timely intervention to prevent further deterioration.
Common Causes and Preventive Measures
Adult hearing loss can result from various factors, including:
- Environmental noise: Prolonged exposure to noisy environments, such as workplaces, lawn mowing, using power tools, or participating in shooting activities.
- Music and entertainment: Listening to loud live or recorded music for extended periods.
- Physiological factors: Excessive earwax buildup, head trauma, or infections.
- Medications and genetics: Side effects of certain medications and hereditary issues.
Preventive measures are crucial, such as wearing protective earplugs in noisy environments to preserve remaining hearing and prevent further damage.
Follow-up Treatment and Recommendations
While it is not possible to fully restore lost hearing, several methods can improve quality of life:
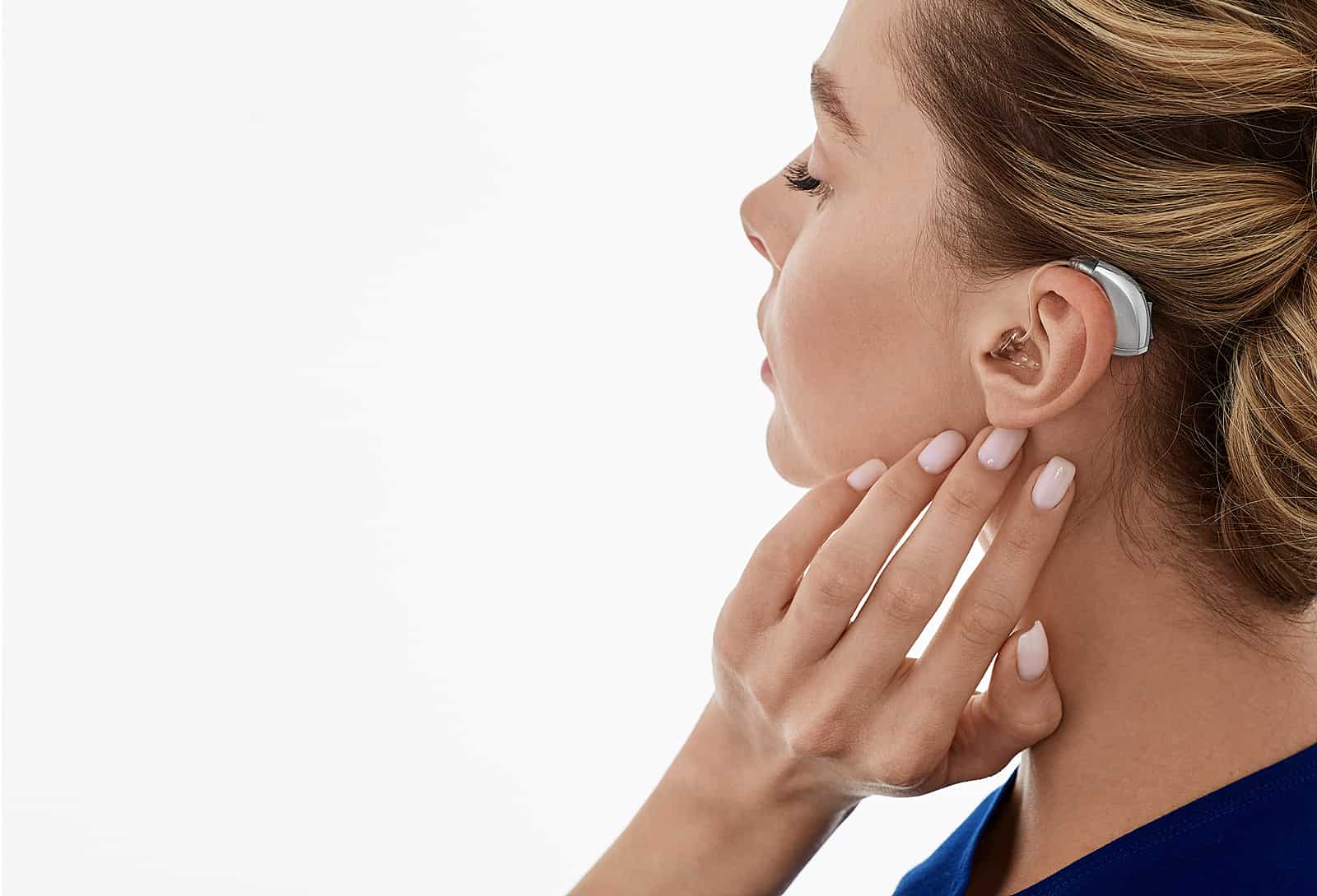
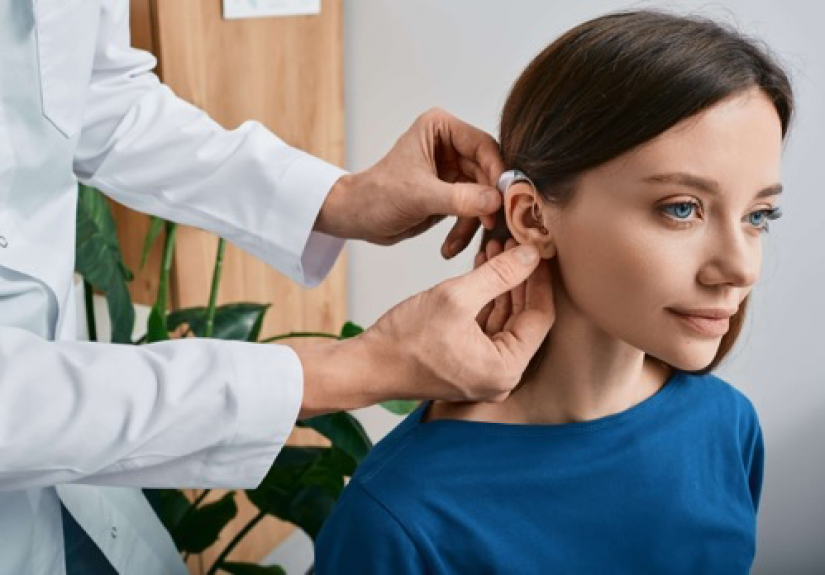
- Assistive devices: If hearing loss is detected, doctors may recommend hearing aids. Modern hearing aids are compact, discreet, and come in various models (e.g., behind-the-ear, in-the-ear, and completely-in-the-canal).
- Speech-enhancing tools: Specialized audio-enhancing devices for phone calls or public use are also available to improve auditory experiences.
- Rehabilitation training: Learning hearing loss detection methods and lip-reading techniques can enhance conversation comprehension.
- Professional consultation: If test results are abnormal, doctors may refer you to an ENT specialist for further diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Regular hearing tests are a vital part of maintaining overall health. By understanding the testing process, correctly interpreting results, and taking appropriate preventive and assistive measures, you can better manage your hearing health and improve your quality of life. Whether to prevent further hearing loss or to receive early intervention, regular check-ups and professional advice are essential.
Stay vigilant, pay attention to your hearing health, and make professional testing and treatment a part of your healthy lifestyle.