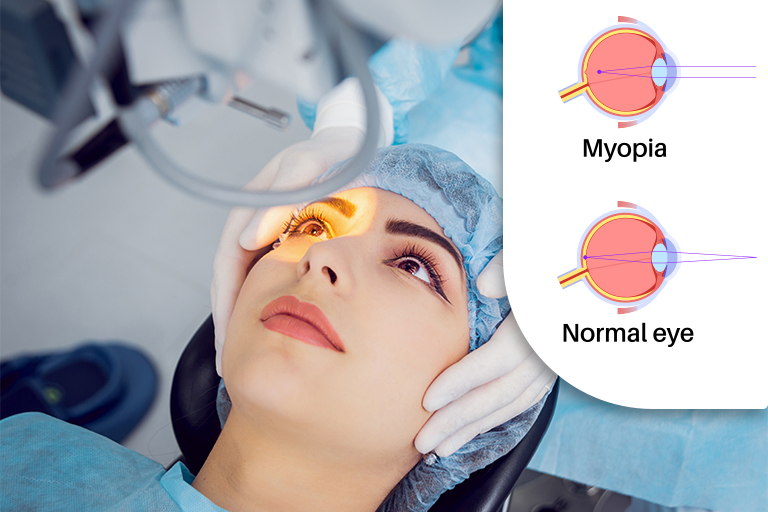
What Is Nearsightedness?
Nearsightedness (myopia) is a vision condition where close objects appear clear, but distant objects become blurry. It occurs due to an elongated eyeball or an abnormal corneal curvature, preventing light from focusing properly on the retina. Studies suggest that myopia is highly hereditary, though environmental factors also play a significant role.
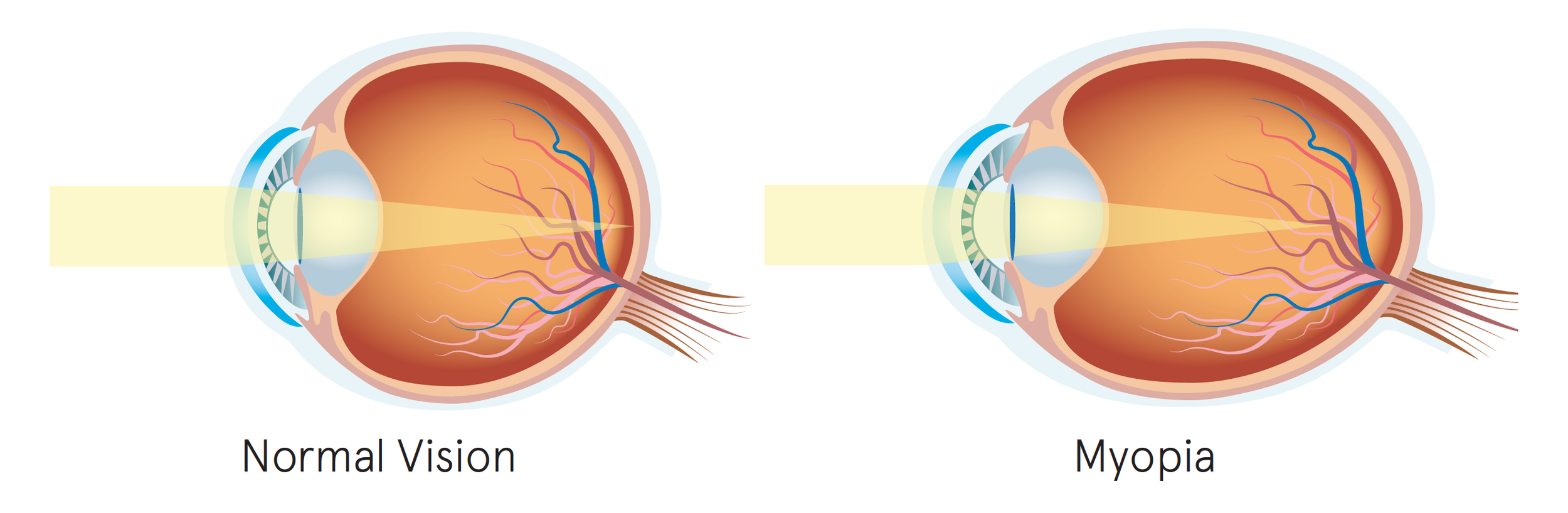
Stages of Nearsightedness
Based on diopter (D) measurement, myopia is categorized into three levels:
- Mild Myopia (≤3D): Minimal nearsightedness that may only require glasses for tasks like driving or viewing distant objects.
- Moderate Myopia (3D–6D): Daily corrective lenses are typically needed for clear vision.
- High Myopia (>6D): Significant vision impairment with an increased risk of conditions like retinal detachment .
Key Factors Affecting Myopia
Several factors contribute to the development and progression of myopia, including:
- Genetics : If one or both parents have myopia, the likelihood of their child developing it increases.
- Environmental Factors: Prolonged near-work activities like reading or screen usage may accelerate myopia progression.
- Lack of Outdoor Time : Research shows that exposure to natural light helps slow the progression of myopia.

Managing and Preventing Myopia
Myopia Control in Children and Teens
Early intervention is crucial to slowing myopia progression in children and teenagers. Recommended strategies include:
- Reducing Screen Time : Limiting prolonged use of digital devices and taking regular eye breaks.
- Increasing Outdoor Activities : At least two hours of outdoor exposure daily has been linked to a lower risk of myopia progression.
- Atropine Eye Drops : Low-dose (0.01%) atropine drops have been shown to effectively slow myopia progression.
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) : Hard contact lenses worn overnight temporarily reshape the cornea and may slow myopia progression.
Myopia Management in Adults
For adults, the best corrective options often include surgical procedures such as:
- LASIK Surgery : Uses laser technology to reshape the cornea for permanent vision correction.
- Photorefractive Keratectomy (PRK) : Similar to LASIK but removes the corneal surface layer, making it suitable for those with thin corneas.
- Implantable Collamer Lenses (ICL) : Recommended for individuals with high myopia who are not candidates for LASIK.
What Level of Myopia Is Considered Legally Blind?
According to legal definitions , a person is considered legally blind if their best-corrected vision is 20/200 or worse. This means that even with corrective lenses, they cannot see objects clearly at 20 feet that a person with normal vision could see at 200 feet. Severe myopia may fall into this category if corrective measures fail to achieve better vision.
Is Nearsightedness Considered a Disability?
Generally, myopia alone is not classified as a disability . However, if it leads to severe complications like retinal detachment or an inability to achieve functional vision even with correction, individuals may qualify for disability benefits. In such cases, they can apply for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and request reasonable accommodations at work, such as magnifiers or assistive technology.
Conclusion
Nearsightedness is a widespread vision condition, but effective prevention and management strategies—such as reducing screen time, increasing outdoor activities, and utilizing myopia control methods —can help slow its progression. For adults, refractive surgery offers a long-term solution for vision correction.
While most people with myopia will not become legally blind , the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) ensures that workplaces and public institutions provide reasonable accommodations . Additionally, individuals who meet the legal blindness criteria may qualify for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) to receive financial assistance.